The Ultimate Guide to Alternative Investment Business
Many people consider alternative investment an exclusive investment class but this is far from the truth. Alternative investment encompasses a wide range of investment assets and strategies and can become a powerful tool to help investors diversify their portfolios, reduce volatility, and grow wealth.
What you will learn in this post:
What is alternative investing?
Alternative investing is a term for a wide group of investments other than publicly-traded investments in stocks, cash, and bonds which are often referred to as traditional investments.
The term “alternative” doesn’t mean that the investment options are uncommon or recent. For example, real estate and commodities are considered alternatives even though they are among the oldest investment types.
Alternatives also include investing via private equity funds and hedge funds that can use derivatives, leverage, invest in illiquid assets, and short-sell.
The most popular types of alternative investments are the following.

Private equity refers to capital investment in private companies or companies not listed on a public exchange.
Private debt is an investment that is not financed by a bank. Companies that provide capital are called private debt funds, and they earn on the repayment of the loan body and interests.
Hedge funds manage the funds of their participants (in most cases, institutional investors) to earn a return on investments by employing various investing strategies.
Real estate investment is one of the most popular investment types that combines the features of bonds – when tenants pay rent, and equity – because its value grows over time.
Commodities are real assets and natural resources such as precious metals, oil, agricultural products, etc. Commodities serve as a hedge against inflation because they are not correlated to equity markets. The prices in this sector depend on the supply and demand and tend to grow when the value of other assets drops.
Collectibles comprise a wide range of items such as coins, art, rare wines, etc. that grow in value over time. Investing in collectibles is risky due to high acquisition costs, the risk that they can be damaged or destroyed, and the lack of any income until the item is sold.
Structured products are pre-packaged investments. They are created by taking a traditional security, the one that pays investors dividend payments (e.g., government or corporate bonds), and replacing the traditional repayment mechanism (dividends) with non-traditional payoffs (derived from the performance of the underlying asset – bonds, stock, etc.).
The main differences between traditional and alternative investments are the following.
| Traditional investment | Alternative investment |
| High liquidity | Lower liquidity |
| Available in public markets | Available in both private and public markets |
| Passive shareholding | Active shareholding |
| Highly correlated to markets | Low correlation to markets, the focus is frequently on inefficient markets |
Why is alternative investing popular?
The interest in alternative investment is growing because this investment type covers a wide range of assets and investment strategies and helps investors to diversify their risk profiles and reduce the potential of negative impact of market crashes.
Alternative investments are not correlated with public markets. That’s why adding them to the portfolio helps to reduce the portfolio’s volatility.
For example, the US farmland is not correlated with most asset classes such as bonds, stocks, real estate, and has a track of maintaining value even during times of high volatility. Gold and silver, two of the most popular alternatives, have also a low correlation to stocks and hold their value well. Real estate can also provide good protection from volatility depending on the location and market conditions.
Another reason why investors are turning to alternatives is that stocks are expensive, and possible returns are not as lucrative as they were.
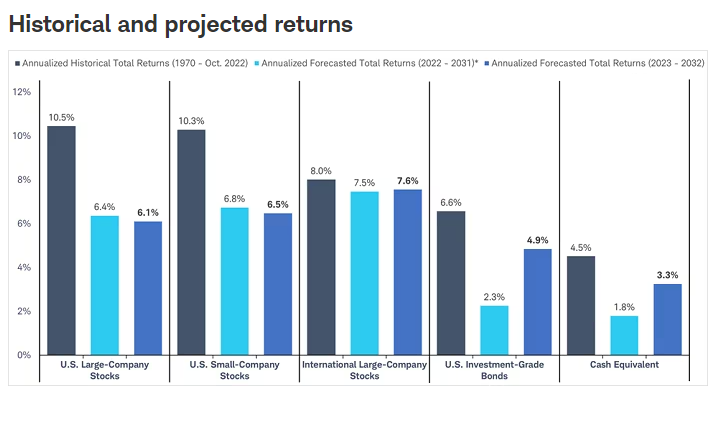
Traditional investment instruments such as government bonds offer low interests that return a yield below inflation. It means that investors cannot count on a traditional portfolio to safeguard from capital loss and ensure a safe return on investment.
That’s why many investors turn to alternatives such as real estate, commodities, farmland, and other asset classes that typically have strong performance through market cycles and ensure profit even when inflation levels surge.
Technological advancement is another factor that has contributed to the rise of alternative investments. Institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals have been benefiting from the opportunities that alternative investment offers for a long time.
But for retail investors, accessing alternatives was impossible due to the lack of transparency, the need for specialized knowledge to understand the investment opportunities, and a high investment threshold. Now, with the development of a big number of specialized platforms that enable different types of investing, alternatives have become accessible to retail investors, too.
How alternative investment funds work?
Alternative investment funds are among the most common alternatives but before you invest in a fund, you shall learn what its objectives are and how it works.

So, alternative investment funds are usually divided into three categories:
- Those that invest in startups, SMEs, and projects with high scaling potential (socially or economically promising)
- Those that invest in equity and debt securities
- Those that aim at short-time returns achieved by employing complex trading strategies.
Category 1
The first category of funds is the following.
Venture Capital Funds
This type of fund pools money from investors and invests in startups with a high scaling potential. Each investor gets a share depending on the sum that the fund invested on his behalf.
Infrastructure Funds
These funds invest in infrastructure development: roads, bridges, communication assets, and so on. Returns from such investments are a combination of capital growth and dividends.
Angel Funds
These funds operate similarly to Venture Capital funds with the main difference being that they invest in startups whose growth is uncertain. Angel Funds build startups and direct them to become profitable.
Social Venture Funds
Social venture funds invest in projects with high social importance, those that try to make a profit and solve environmental problems and social issues.
Category 2
The following types belong to the second category.
Private Equity (PE) fund
PE funds invest in private companies and take a share in their ownership. PE funds normally have an investment horizon varying from 4 to 7 years, after this period is over, they expect to exit the investment with profit.
Debt fund
Debt funds invest in debt instruments of companies that have high potential but need money asap or have a low credit score.
Fund of funds
These funds invest in portfolios of other alternative investment funds rather than creating their own portfolios.
Category 3
Those funds belong to this category that apply various strategies to get returns in a short time.
Hedge fund
This fund pools money from institutional and accredited investors to pull it into international and domestic markets to generate returns. These funds are expensive: they charge a management fee and up to 20% of the generated profit.
Private investment in Public Equity Fund (PIPE)
Private investment in public equity refers to purchasing shares of publicly traded companies with a discount. It allows private investors to get a share in a public company, and the company receives the infusion of funds.
How alternative investment platforms work
Along with funds, specialized platforms enable investing in alternatives. There are several types of alternative investment platforms, and the way a platform provides services to its clients depends on the platform type.
Co-investment platforms
Co-investment platforms collect various investment opportunities in a single online place. Investors can choose whatever project they would like to invest in: a fund, a startup, or an established business. This platform type can include various asset classes such as private equity, venture capital, property, and so on. While some co-investment platforms work with accredited and high-worth investors, there are such services that collaborate with retail investors, too.
This platform type is growing in popularity, with only 24% of global investors using them in 2012, with the value almost tripling to 71% in 2021.
Co-investment platforms charge a range of fees to investors such as a one-time fee whose size depends on the investment type, a yearly management fee, and secondary market fees.
Funds
A fund pulls capital from multiple investors, and a fund manager chooses a range of opportunities and allocates the investors’ funds to get profit.
Depending on the fund type, investments can be made in established companies or startups. Investors have no or little impact on the investments, they rely on the expertise of a fund manager. Funds mostly rely on accredited and institutional investors to pool funds from.
Funds charge a management fee and a performance fee which can be very high (up to 20% of the profit made by the investment).
Crowdfunding platforms
Crowdfunding platforms offer an extensive range of investment opportunities such as real estate, and private equity, among others. Depending on the location, such platforms are regulated differently.
So, in the UK, investment-based crowdfunding is regulated in the same way as retail investment firms. The company shall be registered with the FCA and comply with its minimum threshold conditions, principles, and follow the FCA rules about systems and controls.
In Europe, crowdfunding market regulation is still under development. For now, all the crowdfunding platforms’ activities are regulated by the Regulation on European Service Providers (ECSP) for businesses. This regulation lays down rules for investment-based and lending-based crowdfunding platforms that operate in the EU.
In the USA, investment-based crowdfunding platforms are regulated by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission based on Reg CF.
Alternative Investment Software
If you are considering launching a crowdfunding or alternative investment platform, then LenderKit may be the most optimal alternative investment software to make your platform operate within the shortest time and provide your clients with all the required functionality.
Moreover, you can be sure that your solution will be compliant with the regulation in your region, and that your service will have all the needed integrations such as payment gateways, KYC, eSigns, and others.
To see how the LenderKit alternative investment software works, take a virtual tour, and don’t hesitate to contact us for more information.




